© © 2025 Copyright © Youibot Robotics Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SitemapPrivacy Policy
For efficient navigation,mobile robots need to adopt effective localization strategy. Today we will give you a brief introduction of secondary precise positioning for mobile robots.

Deploy a reflector at a certain height in the factory as the same height as the 2D laser sensor of the AMR. The signal strength of the laser beam emitted by the laser sensor will be higher than other objects in the middle of the environment on the laser reflector. The robot can detect reflector in the environment. And then using the relationship between the relative distance and angle between the reflector and the sensor, combined with the reflector in the environment pre-calibrated position , the robot can calculate the position of the sensor in space to realize the positioning of the AMR in the environment.
The QR code shelf alignment function means that the robot scans the QR code at the bottom of the shelf through the QR code sensor installed in the top center of AMR to obtain the pose of AMR relative to the QR code at the bottom of the shelf. And then AMR moves to the specified position through motion control . At the same time, the module also supports reading the currently scanned QR code ID, and can expand the scanning range of the AMR by configuring the auxiliary code. The pose relative to the center code is calculated through the set offset. In this way, the auxiliary code can be configured so that the AMR can accurately find the center code without scanning the center code.
The QR code positioning process is as follows:
Obtain the image containing the QR code landmark, and segment QR code landmark;
Obtain the coordinates of the three centroid points ABC respectively, and obtain the two centroid points on the diagonal by calculation;
To obtain the coordinates of the midpoint Q of the line connecting the two centroid points on the diagonal line, to judge whether the Q point is in the center of the image, if it is exactly in the center of the image, then the Q point is the position of the precise point of the station; if it is not in the center of the image, Then calculate the deviation distance value, and send the above distance to the AGV for adjustment, so that the Q point in the image is close to the center of the image, that is, the AGV approaches the precise position of the station until it coincides.
It need set the switching point between laser navigation and QR code navigation. At the switching point, there need to be five QR codes which near each other like crosses. The AMR navigates to the QR code, and the AMR switches the navigation map from the laser slam grid map to the QR code map. DM arrays need to be deployed on the guidance route.
the positioning accuracy will not change according to environment changing, which can ensure the stability of positioning.
The accuracy of the QR code is controlled by humans. The mapping accuracy of QR code is higher and more pieces of QR code quantity will get higher the navigation accuracy. Therefore, accurate mapping and reasonable deployment can ensure high navigation repeatability and positioning accuracy
Application QR code feature fusion uses in two scenarios: stable positioning and terminal docking. In the stable positioning application scenario, it is only necessary to switch the QR code group and the navigation QR code. In the terminal docking scenario, all four QR codes are required.
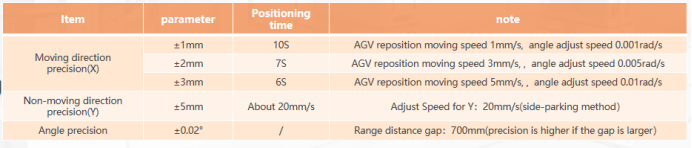
Through the distance measuring sensor and photoelectric sensor installed on the AGV, the distance between the AGV and the positioning plate of the docking machine and the edge position of the reflector are collected to achieve higher-precision secondary positioning, and the secondary positioning accuracy can meet to ±1mm.
The positioning accuracy of pure laser navigation cannot meet the requirements, so sensor positioning is used when high-precision positioning is required; it is usually used for precise docking with several AGVs on the side.
There is a positioning plate with a vertical plane around the secondary positioning position (50mm~600mm), and the plane can be pasted with reflector ;
If the distance between the positioning plate and the sensor is greater than 200mm, it is necessary to replace the photoelectric sensor with a laser sensor.
If the distance between the positioning plate and the sensor is too far, the precise positioning process is easily affected by the external environment.
The primary positioning accuracy must be within ±140mm, otherwise the secondary precise positioning cannot be started (the range of the conventional ranging sensor is limited).
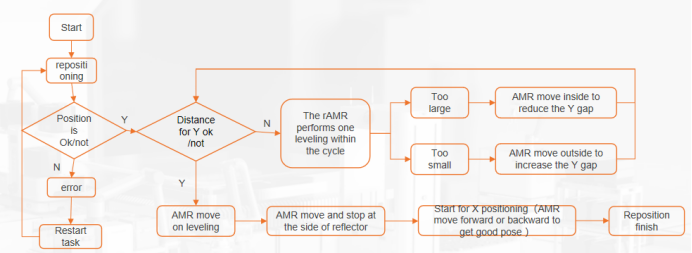
The AMR recognizes the shelf legs through laser sensor to obtain the AMR's pose relative to the center of the shelf during docking process . Since there are many scanned objects similar to shelf legs in the environment, and the four shelf legs are centrally symmetrical. This scheme uses reflectors to wrap all shelf legs of the shelf. And then obtains the information of shelf legs through the reflective intensity information of the reflectors. The pose of the AMR relative to the shelf is obtained by matching the point cloud of the shelf legs. The AMR can enter the shelf from two directions during docking. However, the parameters need to be configured according to the corresponding diagram, and the sensor must scan two legs at least during the docking process. If it can scan more legs, the accuracy will be higher.
Youibot Robotics is a professional mobile robots supplier, who has accumulated rich experience in intelligent logistics in vertical fields such as power plant inspection, vehicle maintenance, automobile and semi-conductor industry intelligence manufacturing. For more information about our mobile robot, please do not hesitate to contact us.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.